5.1 KiB
ALSA Scarlett Control Panel
Scarlett 1st Gen Interfaces
This document describes how to use the ALSA Scarlett Control Panel with the Scarlett 1st Gen interfaces:
- Scarlett 1st Gen 6i6, 8i6, 18i6, 18i8, 18i20
Note: The 1st Gen Scarlett Solo, 2i2, and 2i4 have all their controls accessible from the front panel of the device, and there are no proprietary software controls, so they do not require this control panel software.
Important Driver Limitations
The 1st Gen Scarlett devices have some important limitations in the ALSA driver implementation that you should be aware of:
-
Initial State Detection: The driver cannot read the current state of hardware controls (this appears to be a limitation of the device firmware). When alsa-scarlett-gui starts, what you see will not reflect the actual state of your device unless the controls have previously been set since startup.
-
State Update Issues: The driver only updates the hardware state when it thinks a setting needs to be changed. If the driver incorrectly believes a control is already in the desired state, it won't actually update the control.
Recommended Workaround
To ensure your settings are properly applied:
- Apply a "zero" configuration that sets all controls to values that are not what you desire.
- Then apply your desired configuration
This two-step process helps ensure that the driver actually sends all
commands to the hardware. You may want to create a script using
alsactl for this purpose.
Main Window
The main window is divided into three sections:
- Global Controls
- Analogue Input Controls
- Analogue Output Controls
The particular controls available depend on the interface model.
Note that the View menu option lets you open two other windows which contain additional controls, described in the following sections:
The Levels and Startup windows that are available for later-generation interfaces are not available for 1st Gen interfaces due to driver limitations.
Global Controls
Global controls relate to the operation of the interface as a whole.
Clock Source
Clock Source selects where the interface receives its digital clock from. If you aren't using S/PDIF or ADAT inputs, set this to Internal.
Sync Status
Sync Status indicates if the interface is locked to a valid digital clock. If you aren't using S/PDIF or ADAT inputs and the status is Unlocked, change the Clock Source to Internal.
Analogue Input Controls
Inst
The Inst buttons are used to select between Mic/Line and Instrument level/impedance. When plugging in microphones or line-level equipment (such as a synthesizer, external preamp, or effects processor) to the input, set it to “Line”. The “Inst” setting is for instruments with pickups such as guitars.
Pad
Enabling Pad engages a 10dB attenuator in the channel, giving you more headroom for very hot signals.
Gain
The Gain switch selects Low or High gain for the input channel.
Analogue Output Controls
The analogue output controls let you set the output volume (gain) on the analogue line outputs.
Click and drag up/down on the volume dial to change the volume, use your arrow keys, Home/End/PgUp/PgDn keys, or use your mouse scroll wheel to adjust. You can also double-click on it to quickly toggle the volume between off and 0dB.
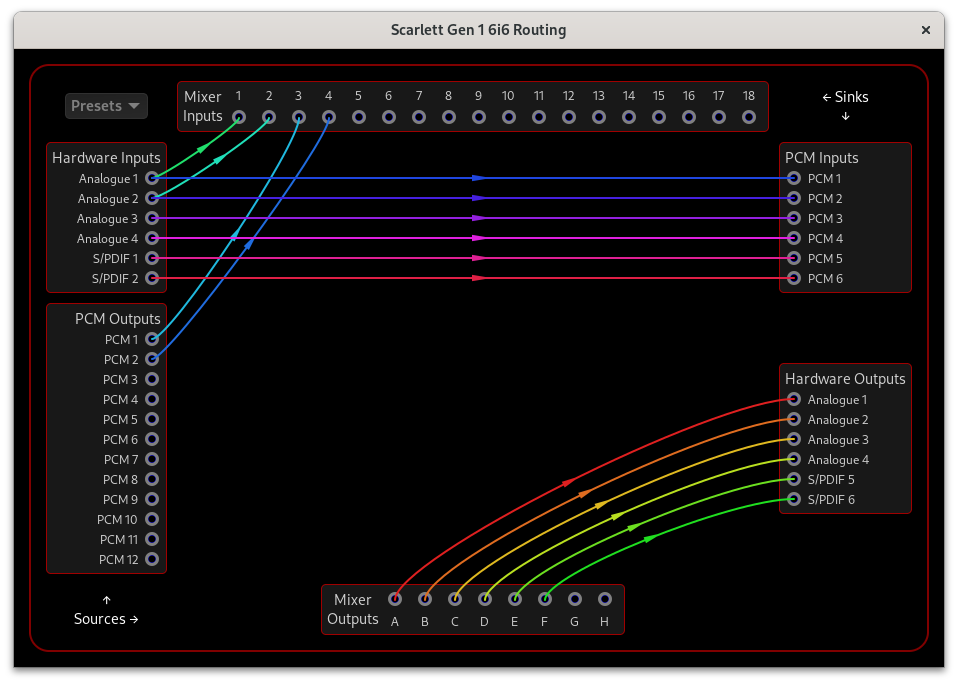
Routing
The routing window allows complete control of signal routing between the hardware inputs/outputs, internal mixer, and PCM (USB) inputs/outputs.
To manage the routing connections:
-
Click and drag from a source to a sink or a sink to a source to connect them. Audio from the source will then be sent to that sink.
-
Click on a source or a sink to clear the links connected to that source/sink.
Note that a sink can only be connected to one source, but one source can be connected to many sinks. If you want a sink to receive input from more than one source, use the mixer inputs and outputs:
- Connect the sources that you want to mix together to mixer inputs
- Connect mixer outputs to the sinks that you want to receive the mixed audio
- Use the Mixer window to set the amount of each mixer input that is sent to each mixer output
The Presets menu can be used to clear all connections, or to set up common configurations:
-
The "Direct" preset sets up the usual configuration using the interface as a regular audio interface by connecting:
- all Hardware Inputs to PCM Inputs
- all PCM Outputs to Hardware Outputs
-
The "Preamp" preset connects all Hardware Inputs to Hardware Outputs.
-
The "Stereo Out" preset connects PCM 1 and 2 Outputs to pairs of Hardware Outputs.
Mixer
If you use the Routing window to connect Sources to Mixer Inputs and Mixer Outputs to Sinks, then you can use the Mixer window to set the amount of each Mixer Input that is sent to each Mixer Output using a matrix of controls.
Click and drag up/down on the gain controls to adjust, or use your mouse scroll wheel. You can also double-click on the control to quickly toggle between off and 0dB.